The Post-9/11 GI Bill is an extremely generous education benefit for military veterans who served on active duty after September 10, 2001. But what exactly does this benefit pay for? Here’s a comprehensive look at all the different things the Post-9/11 GI Bill helps cover.
Tuition and Fees
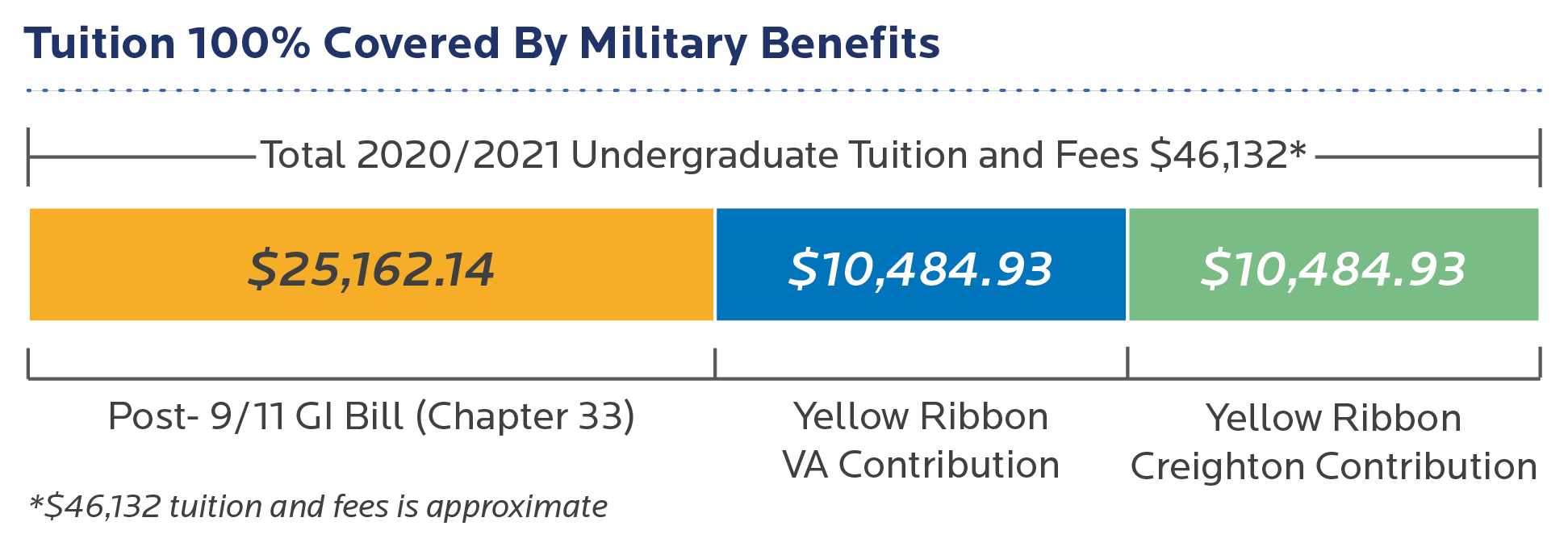
One of the biggest expenses the Post-9/11 GI Bill helps with is tuition and fees. If you qualify for 100% of the benefit, the GI Bill will pay the full cost of in-state tuition and fees at public schools. For private schools and out-of-state students the GI Bill pays up to a yearly maximum amount per academic year.
In 2022, the maximum coverage amounts were:
- $26,804.81 per academic year for private schools
- $27,936.71 per academic year for out-of-state students at public schools
These maximum amounts are adjusted annually based on the cost of living
The Post-9/11 GI Bill will cover all net tuition and fees after scholarships and aid are applied. This makes it an extremely valuable benefit that can minimize student loan debt.
Monthly Housing Allowance
Another major expense covered by the Post-9/11 GI Bill is a monthly housing allowance. This helps veterans cover housing costs near the school they are attending.
The housing allowance amount is equal to the military Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) for an E-5 with dependents based on the zip code for your school. The amount you receive depends on your GI Bill eligibility percentage and rate of pursuit (hours enrolled).
For example, if you qualify for 80% of the GI Bill benefit and are taking 9 credits when 12 is considered full-time, your monthly housing payment would be:
BAH for your zip code x 80% GI Bill eligibility x 75% rate of pursuit
The housing allowance is a huge help in affording rent or room and board while in school.
Book and Supply Stipend
The Post-9/11 GI Bill also provides a stipend of up to $1,000 per academic year to help pay for books, laptops, and other supplies you need for your education. This stipend is paid proportionally based on your enrollment each term.
The book stipend can be used to buy required books and supplies at your university bookstore or get a new computer. It provides additional financial assistance beyond just tuition and housing costs.
Yellow Ribbon Program
For veterans attending private schools or out-of-state students with costs exceeding the GI Bill’s maximum coverage, the Yellow Ribbon Program can help bridge the gap.
Under this program, your school will contribute a specified amount towards tuition and fees and VA will match that amount. Over 1,000 colleges and universities participate in the Yellow Ribbon Program.
Rural Benefit
If your school is in a rural area, you may qualify for a one-time $500 benefit payment. To be eligible, your school must be in a county with 6 or less people per square mile.
This benefit helps veterans in rural areas with education costs and encourages them to relocate to attend school if needed.
College Fund and Transferability
The Post-9/11 GI Bill allows veterans to transfer benefits to a spouse or dependent children. Eligible dependents receive the College Fund kicker payment of $600 per month on top of other benefits.
Transferring benefits and the College Fund gives veterans the opportunity to share their education benefits with family members.
Licensing, Certification, and Testing
The Post-9/11 GI Bill will pay for licensing and certification tests and preparatory courses needed for your career. This includes exams like the LSAT, GRE, SAT, etc.
It’s a great benefit for veterans pursuing careers requiring licenses, certifications or specialized tests.
Tutoring and Other Services
To help you succeed academically, the Post-9/11 GI Bill can provide up to $100 per month for tutoring or other academic support services.
It will also help cover the cost of any required fees like lab fees or expenses for required uniforms, equipment, and supplies.
Types of Training Covered
Beyond just college degrees, the Post-9/11 GI Bill will pay for many types of job training programs including:
- Vocational training
- Flight training
- Apprenticeships
- On-the-job training
- Non-college degrees
It provides flexible options beyond a traditional 4-year college degree.
Monthly Stipend for STEM Programs
Veterans pursuing science, technology, engineering, or math degrees may qualify for an additional monthly stipend through the Edith Nourse Rogers STEM Scholarship. This provides up to 9 extra months of GI Bill funding to help veterans complete STEM programs.
Work-Study Program
Veterans can earn additional income while in school through VA work-study programs. These allow you to work part-time for an hourly wage at approved work-study positions. It provides veterans with valuable work experience and income during their education.
No Time Limit for New Vets
One of the best parts of the Post-9/11 GI Bill is that there is no time limit to use benefits for veterans who left service on or after January 1, 2013.
The “Forever GI Bill” removed the 15 year time limit. Now veterans who served after 2013 can use their benefits at any time in the future.
A Lifetime of Benefits
With numerous provisions covering tuition, housing, books, testing, training, and more, the Post-9/11 GI Bill provides veterans with a lifetime of education benefits.
It allows veterans to get degrees, pursue careers, and gain skills without being overburdened by student loan debt. The GI Bill opens doors to new opportunities and financial security.
For those who served our country, it’s a token of thanks and investment into their futures. The Post-9/11 GI Bill pays for schooling, training, and so much more to help veterans succeed.
Full rates for school and training programs
Effective August 1, 2024, to July 31, 2025
We’ll send your tuition and fees directly to your school or training program.
The amounts listed here are the maximum amounts we’ll pay this academic year for each type of school or training program. If you’re eligible for a percentage of the full benefit, multiply the amount by your percentage. This will give you the maximum amount we’ll pay this academic year.
Find out the full rate based on what type of school you’re attending:
- Public institution of higher learning (like a state university or community college): We’ll pay the net tuition and mandatory fees. You may be able to get in-state tuition rates at a public school even if you haven’t lived in the state where the school is located.Learn more about in-state tuition rates
- Private institution of higher learning: We’ll pay the net tuition and mandatory fees up to $28,937.09.
- Foreign institution of higher learning (a college or university, whether public or private, in a country outside the U.S.): We’ll pay the net tuition and mandatory fees up to $28,937.09 in U.S. dollars.
- Non-college degree programs (specific training programs like HVAC repair, truck driving, EMT, or beautician school): We’ll pay the net tuition and mandatory fees up to $28,937.09.
- Flight training (a non-degree certificate or rating program): We’ll pay the net tuition and mandatory fees up to $16,535.46.
- Correspondence school (usually courses provided by mail that you complete at your own pace): We’ll pay the net tuition and mandatory fees up to $14,055.13.
You may be eligible for money to help pay for your housing while you’re studying. If you’re eligible for monthly housing allowance (MHA), we’ll pay you this allowance at the end of each month.
We’ll pay you a percentage of the full monthly housing allowance (called a “prorated payment”) based on these 2 factors:
- The percentage of Post-9/11 GI Bill benefits you’re eligible for, and
- How many credits you’re taking or how many clock hours you’re scheduled to attend per week
You’re not eligible for an MHA payment if any of these are true:
- You’re on active duty, or
- You’re a spouse using transferred benefits while the Veteran is on active duty, or
- You’re in school half time or less than half time, or
- You’re taking correspondence training or flight training, or
- You’re on break from school
We base your MHA on the monthly military Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) rates for an E-5 with dependents. This is called the resident MHA. We use the 2024 rates to calculate the MHA you get between August 1, 2024, and July 31, 2025.
You can use the Defense Department (DOD) lookup tool on the Defense Travel Management Office website to find out how much money you may be eligible to receive for housing. You’ll need the zip code for your school to get started.
We base your monthly housing allowance on the national average.
We’ll pay you up to $1,177.50 (equal to half the national average for MHA). This is the maximum amount we’ll pay you each month.
Note: If you take at least one class in person while taking other online learning classes, you may be eligible for the higher resident MHA.
We base your monthly housing allowance on the national average.
We’ll pay you up to $2,355.00 (equal to the national average for MHA). This is the maximum amount we’ll pay you each month.
Money to help you move from a rural area
If you need to relocate from a highly rural area so you can attend school, we may give you a one-time payment of $500 to help with your moving expenses.
You may be eligible for this Post-9/11 GI Bill rural grant if the description listed here is true for you.
This must be true:
You live in a county with no more than 6 people per square mile, as determined by the most recent U.S. census.
And one of these must be true:
- You need to physically relocate at least 500 miles away from your home to attend school, or
- You need to travel by air to physically attend school because you don’t have the option to travel by car, train, bus, or other ground transportation
If your college or university tuition costs more than the maximum payment, you may be eligible for added payments through the Yellow Ribbon Program.
If you’re struggling with your coursework, you may be eligible for up to $100 per month, up to $1,200 total, for tutorial assistance.Learn more about tutorial assistance
If you’re enrolled in a school or professional training program, you may be eligible to earn extra money through a part-time job related to VA work.
How Much Money I Made Using The Post 9/11 GI Bill
FAQ
How much does the post-9/11 GI Bill cover per year?
What exactly does the GI Bill pay for?
What does the GI Bill not cover?
